The Benefits of Good Water Quality
Water and Health Are Linked

Bad water is bad for you, but safe water is key to life — and good for you! Water has so many health benefits that the U.S. Centers for Disease Control & Prevention (CDC) recommends drinking eight 8-ounce glasses of water every day.
Water and health are linked. According to the CDC, the top causes of disease outbreaks related to drinking water are Giardia intestinalis, hepatitis A, norovirus, andShigella. Bad as that sounds, it’s far from a complete list. There are also health risks related to water contaminated with organic and inorganic matter, other bacteria and viruses and other pollutants.
Some studies link high levels of lead in drinking water to delays in physical and mental development, short attention spans, and learning difficulties in children. There’s also evidence that arsenic in drinking water can lead to nerve, heart, skin, and blood vessel damage. And Cryptosporidium is responsible for potentially life-threatening diarrhea.
Still, water is essential. The human body is, after all, 70% water, and although a human being can survive a month or more without food, a week without water can be fatal.
Good for Appliances, Too

High quality water is good for your home and appliances. Softened water can save you money by keeping appliances at top efficiency, and making them last longer. The amount of dish and laundry detergent you use can be cut by half, or even more, if you use softened water. You can also lower wash temperatures from hot to cold without a drop in performance, according to two other independent studies.
A 2009 study commissioned by the Water Quality Research Foundation (WQRF) and conducted by the Battelle Memorial Institute found that adding a water softener helps water heaters and major appliances operate as efficiently as possible, while preventing clogs in showerheads, faucets, and drains. For example, researchers ran dishwashers and washing machines for 30 days and 240 wash cycles. They ran softened water through half of the units, while using a hard water source for the others. At the end of the month, the washers using softened water were nearly free of scale buildup, but the washers using hard water required scale removal to work well.
As for water heaters, the researchers found that when they used softened water, the units maintained their original factory efficiency rating for as long as 15 years. Running hard water through the units cut efficiency by up to 48 percent. Scale buildup shortened the lifespan of the heating elements inside electric water heaters, and some tankless water heaters using hard water failed after just 1.6 years.
The researchers found that showerheads performed well on soft water, but those running with hard water lost 75 percent of their flow rate in less than 18 months. When running hard water through faucets, the strainers on the faucets clogged within 19 days.
Studies conducted by the independent test firm Scientific Services S/D, Inc., of New York, revealed the following benefits of softened water:

- In washing machines, softened water can reduce detergent use by 50% and save energy by making it possible to wash in cold (60ºF) rather than hot (100ºF) water. Cold water washes with softened water achieved the same or better results when it came to removing stains and whitening fabrics.
- In dishwashers, softened water can achieve the same cleaning results as unsoftened while using less than half as much detergent.

 In America, the average family uses about 400 gallons of water per day, 30 percent of that is devoted to outdoor uses. More than half of that outdoor water is used for watering lawns and gardens. Unfortunately, inefficient watering practices can waste a lot of water on gardening and lawn care. When gardening it is important to know how much water your plants need and how often they need to be watered.
In America, the average family uses about 400 gallons of water per day, 30 percent of that is devoted to outdoor uses. More than half of that outdoor water is used for watering lawns and gardens. Unfortunately, inefficient watering practices can waste a lot of water on gardening and lawn care. When gardening it is important to know how much water your plants need and how often they need to be watered.
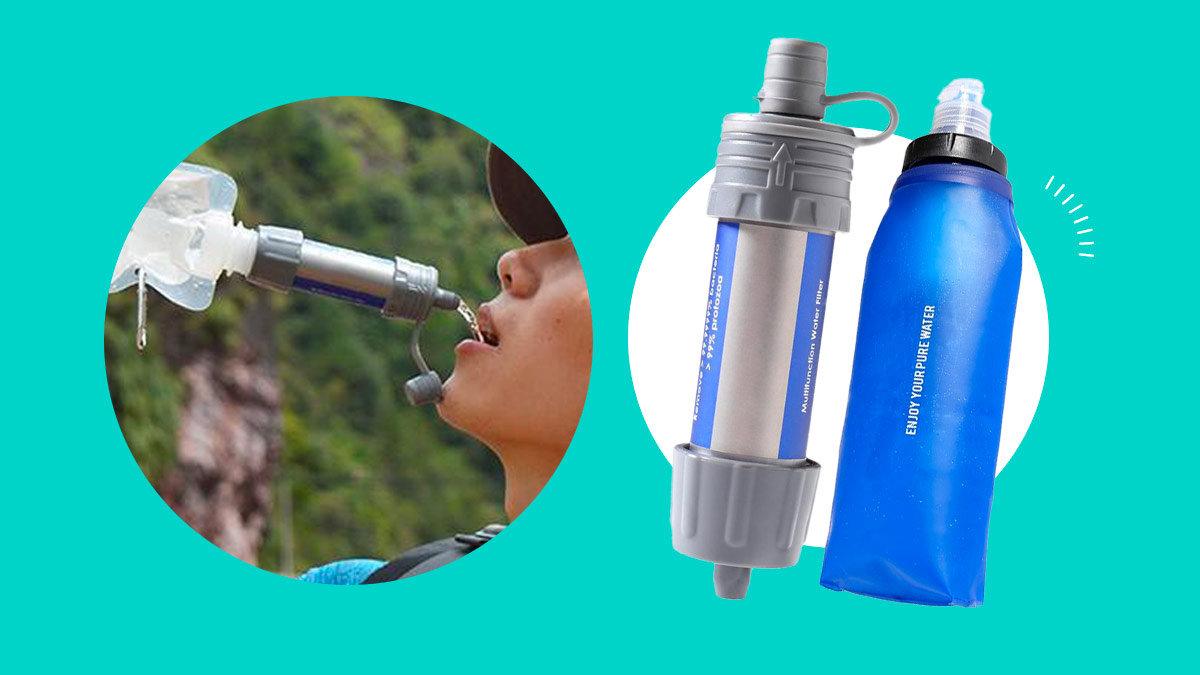












:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/purnewadvancedfilter-566774ae5f9b583dc3c492ff.jpg)

